截止目前,引用Bioss产品发表的文献共24858篇,总影响因子116841.414分,发表在Nature, Science, Cell以及Immunity等期刊的文献共58篇,合作单位覆盖了清华、北大、复旦、华盛顿大学、麻省理工学院、东京大学以及纽约大学等国际知名研究机构上百所。
我们每月收集引用Bioss产品发表的文献。若您在当月已发表SCI文章,但未被我公司收集,请致电Bioss,我们将赠予现金鼓励,金额标准请参考“发文章 领奖金”活动页面。
近期收录2023年4月引用Bioss产品发表的文献共288篇(图一,绿色柱),文章影响因子(IF) 总和高达2009.871,其中,10分以上文献47篇(图二)。
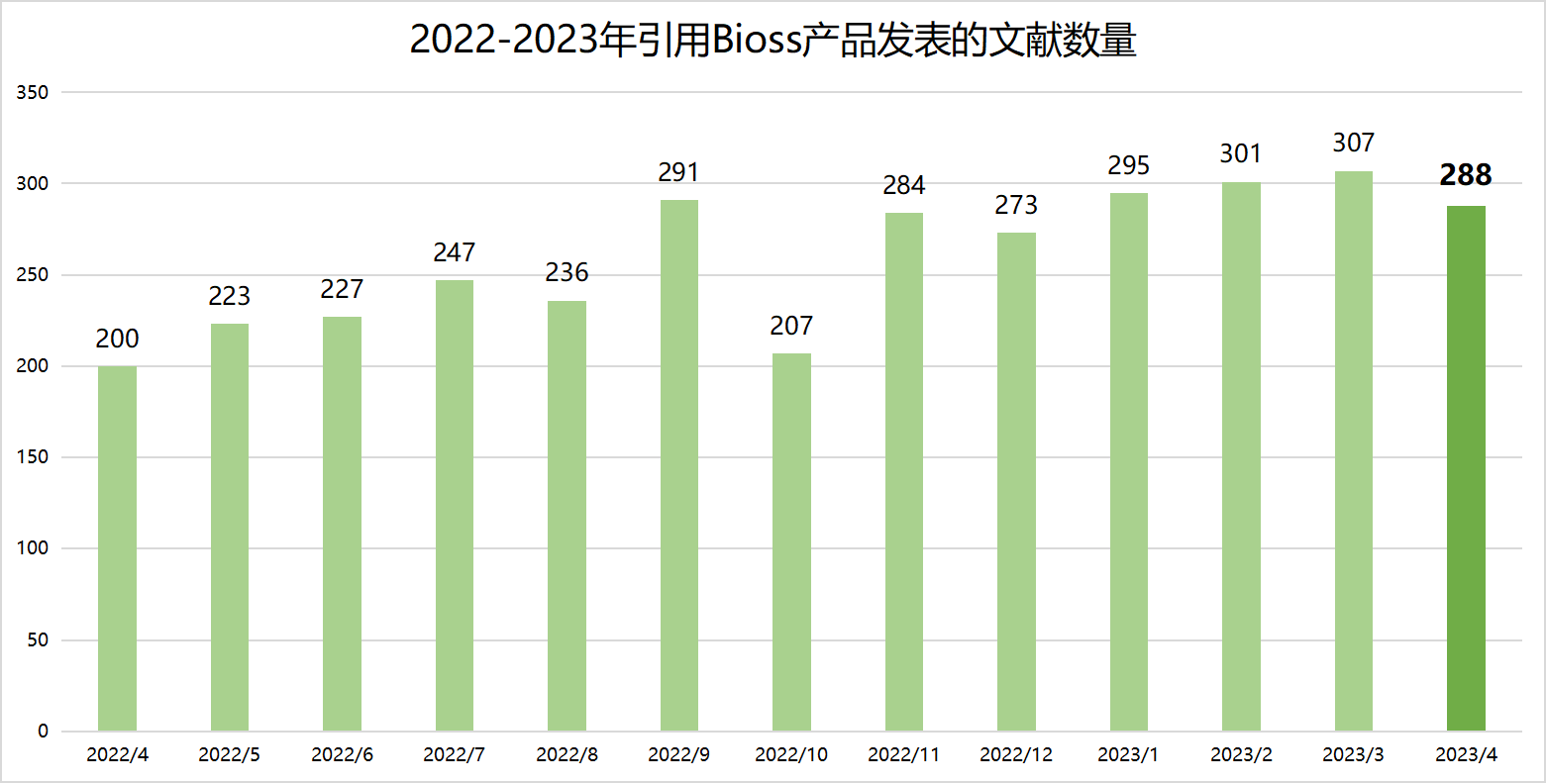
图一
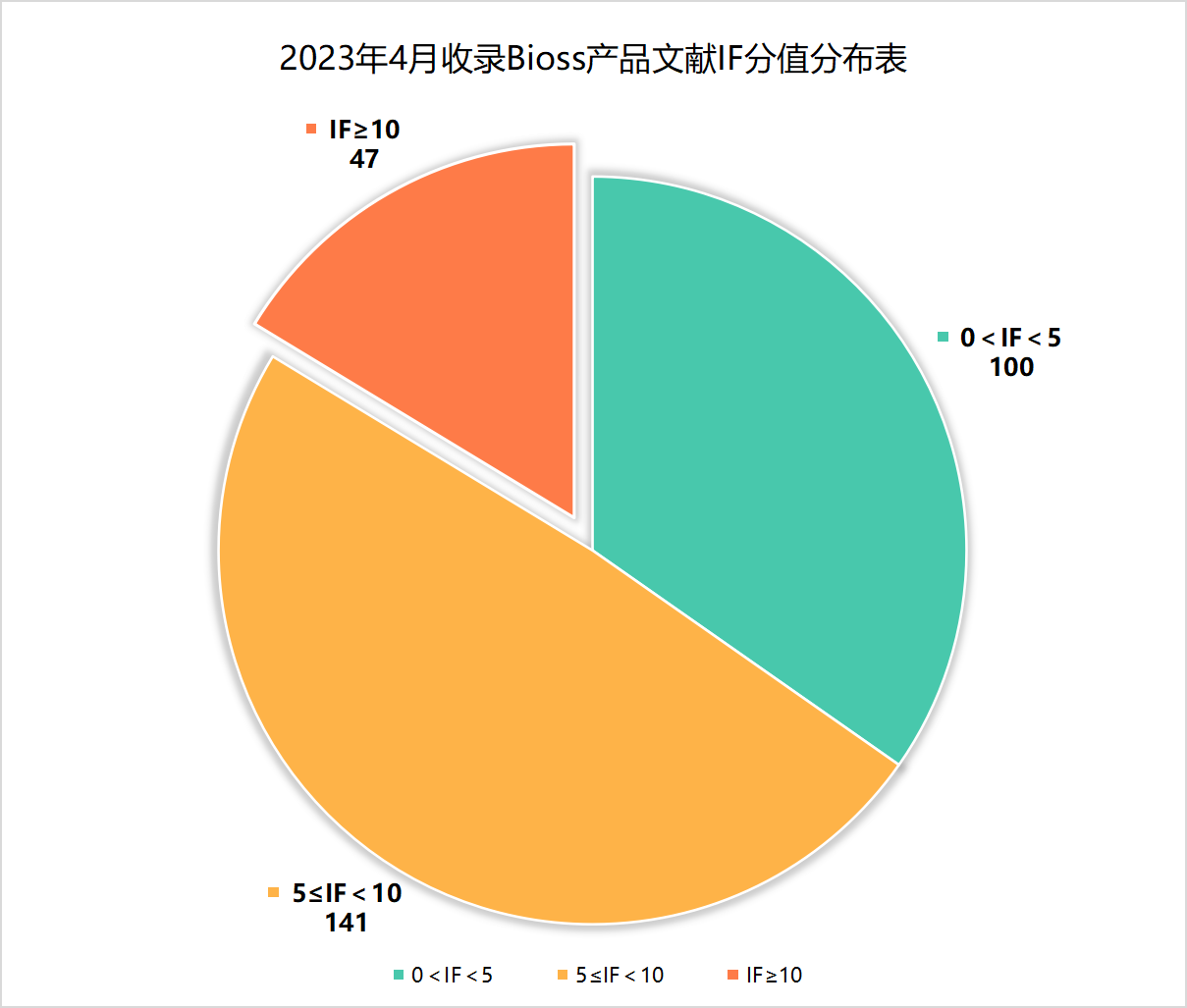
图二
本文主要分享引用Bioss产品发表文章至Nature Nanotechnology, Immunity, Cancer Cell等期刊的5篇 IF>15 的文献摘要,让我们一起欣赏吧。
Cell Discovery [IF=38.079]
文献引用抗体:bsm-41516M
Mouse Anti- SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike RBD mAb | WB
作者单位:北京大学未来技术学院生物医学工程系
摘要:Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection has elicited a worldwide pandemic since late 2019. There has been ~675 million confirmed coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases, leading to more than 6.8 million deaths as of March 1, 2023. Five SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs) were tracked as they emerged and were subsequently characterized. However, it is still difficult to predict the next dominant variant due to the rapid evolution of its spike (S) glycoprotein, which affects the binding activity between cellular receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and blocks the presenting epitope from humoral monoclonal antibody (mAb) recognition. Here, we established a robust mammalian cell-surface-display platform to study the interactions of S-ACE2 and S-mAb on a large scale. A lentivirus library of S variants was generated via in silico chip synthesis followed by site-directed saturation mutagenesis, after which the enriched candidates were acquired through single-cell fluorescence sorting and analyzed by third-generation DNA sequencing technologies. The mutational landscape provides a blueprint for understanding the key residues of the S protein binding affinity to ACE2 and mAb evasion. It was found that S205F, Y453F, Q493A, Q493M, Q498H, Q498Y, N501F, and N501T showed a 3–12-fold increase in infectivity, of which Y453F, Q493A, and Q498Y exhibited at least a 10-fold resistance to mAbs REGN10933, LY-CoV555, and REGN10987, respectively. These methods for mammalian cells may assist in the precise control of SARS-CoV-2 in the future.
JOURNAL OF HEPATOLOGY [IF=30.083]
文献引用抗体:bs-1278R
Anti-8-OHdG (DNA/RNA Damage) pAb | IHC
作者单位:美国明尼苏达州罗切斯特市梅奥诊所生物化学和分子生物学部
摘要:Background & Aims
The prevalence of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)-driven hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is rising rapidly, yet its underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Herein, we aim to determine the role of hypoxia-inducible lipid droplet associated protein (HILPDA)/hypoxia-inducible gene 2 (HIG2), a selective inhibitor of intracellular lipolysis, in NASH-driven HCC.
Methods
The clinical significance of HILPDA was assessed in human NASH-driven HCC specimens by immunohistochemistry and transcriptomics analyses. The oncogenic effect of HILPDA was assessed in human HCC cells and in 3D epithelial spheroids upon exposure to free fatty acids and either normoxia or hypoxia. Lipidomics profiling of wild-type and HILPDA knockout HCC cells was assessed via shotgun and targeted approaches. Wild-type (Hilpdafl/fl) and hepatocyte-specific Hilpda knockout (HilpdaΔHep) mice were fed a western diet and high sugar in drinking water while receiving carbon tetrachloride to induce NASH-driven HCC.
Results
In patients with NASH-driven HCC, upregulated HILPDA expression is strongly associated with poor survival....
ADVANCED FUNCTIONAL MATERIALS [IF=19.924]
文献引用抗体:bs-0287R
Anti-His tag pAb | WB
作者单位:中国药科大学生命科学与技术学院江苏省生物药物可提取性重点实验室和天然药物国家重点实验室
摘要:The efficient delivery of biologics into cells provide unique opportunities to modulate intracellular targets not druggable by conventional small molecules. The supercharged polypeptide (SCP) has become a novel intracellular delivery system due to their special advantages, including enhanced delivery efficiency and serum tolerance. However, owing to their cationic charge and non-specificity characteristics, the in vivo application of SCP is limited. Here, an activatable SCP (ASCP) with a pH-sensitive charge shielding sequence (CSS), a protease cleavage site, and SCP are engineered. This system shows the potential to reduce the non-specific binding and effectively deliver various cargo (peptide, protein, small molecule, and siRNA) into the cytosol not only in vitro but also in vivo. Furthermore, an ASCP fusion protein is designed to co-delivery of peptide (KLA)/siRNA (IKBKE) with different tumorigenesis pathways to triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) for optimal therapeutic outcomes. It is believed that ASCP delivery system will facilitate the development of bioactive molecules for use against intracellular targets. This simple yet versatile delivery system can also pave the way for the co-delivery of multiple therapeutic cargos to address the emerging needs of combination cancer therapy.
NUCLEIC ACIDS RESEARCH [IF=19.16]
文献引用抗体:bs-10966R
Anti-Actin pAb | WB
作者单位:中国广东广州中山大学附属第一医院儿科
摘要:CST (CTC1-STN1-TEN1) is a telomere associated complex that binds ssDNA and is required for multiple steps in telomere replication, including termination of G-strand extension by telomerase and synthesis of the complementary C-strand. CST contains seven OB-folds which appear to mediate CST function by modulating CST binding to ssDNA and the ability of CST to recruit or engage partner proteins. However, the mechanism whereby CST achieves its various functions remains unclear. To address the mechanism, we generated a series of CTC1 mutants and studied their effect on CST binding to ssDNA and their ability to rescue CST function in CTC1−/− cells. We identified the OB-B domain as a key determinant of telomerase termination but not C-strand synthesis. CTC1-ΔB expression rescued C-strand fill-in, prevented telomeric DNA damage signaling and growth arrest. However, it caused progressive telomere elongation and the accumulation of telomerase at telomeres, indicating an inability to limit telomerase action. The CTC1-ΔB mutation greatly reduced CST-TPP1 interaction but only modestly affected ssDNA binding. OB-B point mutations also weakened TPP1 association, with the deficiency in TPP1 interaction tracking with an inability to limit telomerase action. Overall, our results indicate that CTC1-TPP1 interaction plays a key role in telomerase termination.
ACS Nano [IF=18.027]
文献引用抗体:bs-0295G-HRP
Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L / HRP | WB
作者单位:北京理工大学生命科学学院
摘要:The intrinsic features and functions of platelets and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) indicate their great potential in the treatment of intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). However, neither of them can completely overcome ICH because of the stealth process and the complex pathology of ICH. Here, we fabricate hybrid cells for versatile and highly efficient ICH therapy by fusing MSCs with platelets and loading with lysophosphatidic acid-modified PbS quantum dots (LPA-QDs). The obtained LPA-QDs@FCs (FCs = fusion cells) not only inherit the capabilities of both platelets and MSCs but also exhibit clearly enhanced proliferation activated by LPA. After systemic administration, many proliferating LPA-QDs@FCs rapidly accumulate in ICH areas for responding to the vascular damage and inflammation and then efficiently prevent both the primary and secondary injuries of ICH but with no obvious side effects. Moreover, the treatment process can be tracked by near-infrared II fluorescence imaging with highly spatiotemporal resolution, providing a promising solution for ICH therapy.